What a Day! Tag der Deutschen Einheit 2025 💪🤖
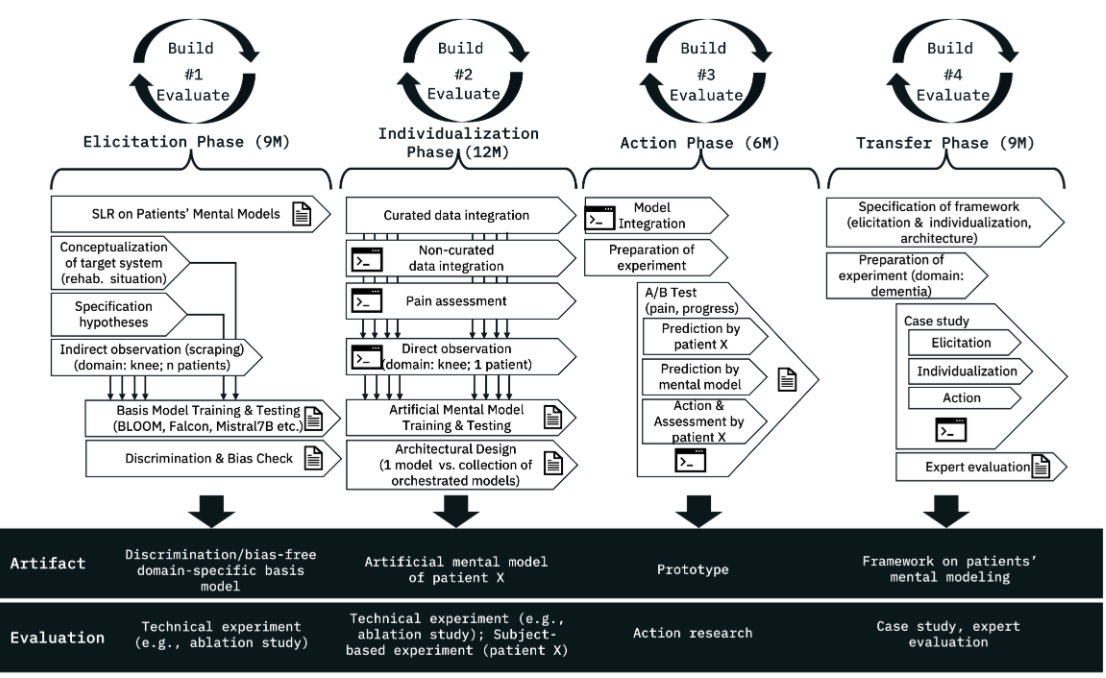
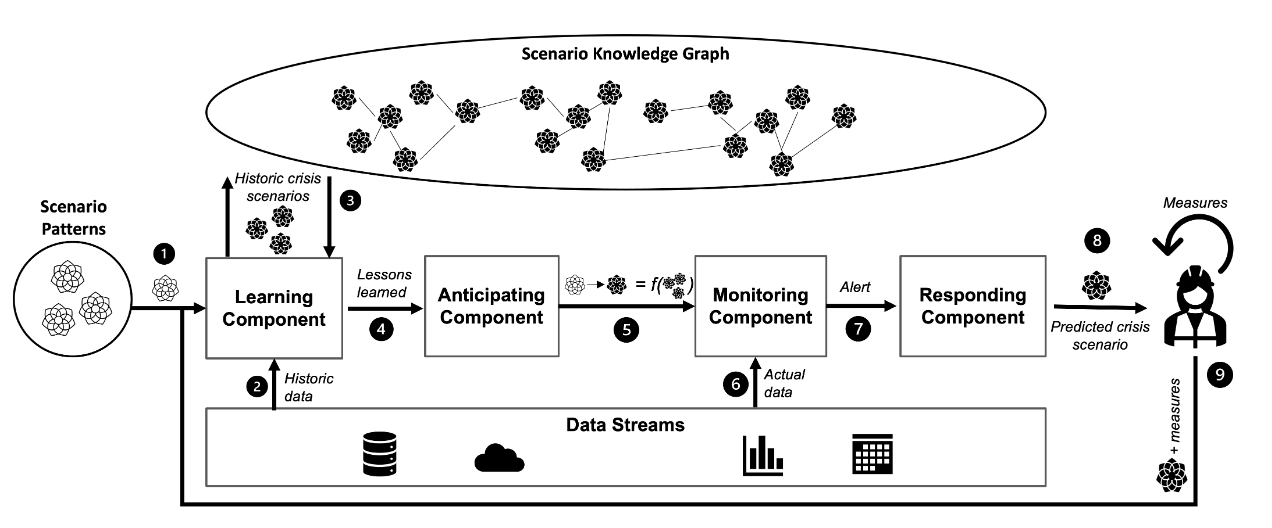
At Tag der Deutschen Einheit (Germany's Unity Day) celebrations in Saarbrücken, our department showcased Mentalytics, an AI system based on Large Language Models (LLMs) that predicts participants' mental states and detects actual pain and effort to p ...