The Chair of Business Informatics at Saarland University and the research department Smart Service Engineering at the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), led by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Wolfgang Maaß, investigate artificial intelligence can be used for adaptive service designs and innovative business solutions. In collaboration with research and industrial partners, results are applied in domains such as industrial manufacturing, crisis management, healthcare, wellness, and sports, among others.
Latest News
| Final Meeting of the QUASIM Research Project at DFKI Saarbrücken | |

|
Advancing Quantum Computing for Manufacturing Simulation The final meeting of the research project QUASIM: QUANTUM COMPUTING ENHANCED SERVICE ECOSYSTEM FOR SIMULATION IN MANUFACTURING took place at the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI) in Saarbrücken. This collaborative project aimed to explore how quantum computing can enhance simulation technologies in the manufacturing sector, particularly within the metalworking industry. With over 390,000 companies and approximately 3.7 million employees, the metalworking industry represents the largest secondary sector within the EU-28 (Eurostat, Sectoral Analysis of Key Indicators). Machining is one of the most significant manufacturing technologies in this sector, crucial for industries such as tool and mould making, the semiconductor industry, and engine construction. Given the industry's reliance on machining, companies are continuously striving for higher quality, productivity, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. Quantum Computing for Manufacturing Optimization State-of-the-art manufacturing processes can be optimized with the support of computer simulations, which are often time-consuming and expensive. QUASIM focuses on mathematical problems that frequently arise in industrial simulations, developing quantum algorithms that can solve these problems faster or with less computational storage than classical approaches. The research aims to improve scalability based on problem-dependent parameters, such as the number of equations to solve or the desired accuracy. By considering large-scale mathematical problems common in manufacturing simulations, QUASIM aims to revolutionize computational efficiency and industrial applicability. Use Cases of Quantum Computing in Manufacturing Use Case 1: Milling Process Optimization Milling is a metal-cutting manufacturing process where a multi-toothed tool rotates to create various workpiece surfaces. Unlike other processes such as turning or drilling, milling features constant cutting interruptions, which can cause dynamic excitations leading to vibration marks on the workpiece surface. To address this issue, dynamic process stability simulations are performed to analyze vibrations and optimize milling process design, particularly for thin-walled components. In QUASIM, a dexel-based engagement simulation is followed by a finite element method (FEM) simulation workflow, involving: - IPW (in-process workpiece) conversion from dexel to solid - Meshing process - Modal analysis A key challenge is the solution of eigenvalue problems in modal analysis, which are computationally intensive. Quantum algorithms are being investigated to accelerate eigenvalue problem solving, potentially reducing simulation time and improving accuracy in milling process optimization. Use Case 2: Optimizing Laser Cutting Through Thermal Expansion Analysis In laser cutting, accurately predicting and managing thermal expansion in metal sheets is critical to ensuring precision and preventing defects. The heat generated by the laser causes thermal deformation, which affects the final shape and quality of the manufactured component. Simulations are essential for modeling these effects, but traditional finite element method (FEM)-based simulations are computationally expensive. QUASIM investigates quantum-enhanced approaches for thermal expansion analysis, focusing on solving large-scale differential equations governing heat transfer and deformation. Quantum algorithms are being explored to: - Accelerate the solution of heat diffusion equations - Improve the accuracy of temperature distribution predictions - Enhance optimization of laser parameters for high-precision cutting By leveraging quantum machine learning (QML) techniques, the project aims to develop faster and more accurate thermal simulations, enabling manufacturers to reduce waste, increase precision, and improve energy efficiency in laser-based manufacturing processes. Quantum Computing as a Game Changer Initial research within QUASIM suggests that quantum computing offers significant advantages in addressing these challenges. Quantum mechanical principles have the potential to: - Accelerate numerical simulations dramatically - Improve simulation accuracy through quantum machine learning (QML) - Enable real-time optimization of machining processes These findings indicate that quantum-enhanced computing could revolutionize manufacturing by making high-fidelity simulations feasible for industrial use. Participants and Key Stakeholders The final meeting brought together key stakeholders from academia, industry, and government, reflecting the project's broad impact and interdisciplinary nature. Notable participants included: - Wolfgang Förster, Staatssekretär des Finanz- und Wissenschaftsministeriums des Saarlandes - Dr. Glasmacher (BMWK) - Dr. Grass (DLR) - Prof. Frank Wilhelm-Mauch (FZJ) - Prof. Wolfgang Maaß (DFKI, Project Coordinator) - Dr. Tobias Stollenwerk (FZJ) - Dr. Valentina König (moduleworks) - Sven Danz (FZJ) - Alejandro Delgadillo (moduleworks) - Marco Kulig (TRUMPF) - Rivan Ruguhbar (FZJ) - Anika Rusch (DFKI) - Stefan Schröder (Fraunhofer IPT) - Nirav Shinoy (DFKI) - Hannah Stein (DFKI) The meeting marked the culmination of years of research and innovation, demonstrating the potential of quantum computing to transform manufacturing simulation. As the industry moves forward, continued collaboration between research institutions, technology providers, and manufacturers will be essential in bringing these advancements from the lab to real-world applications.
Published on: 2025-02-18
🔗
|
| Presentation of Project INTE:GRATE to the Transport Committee of the Saarland State Parliament | |
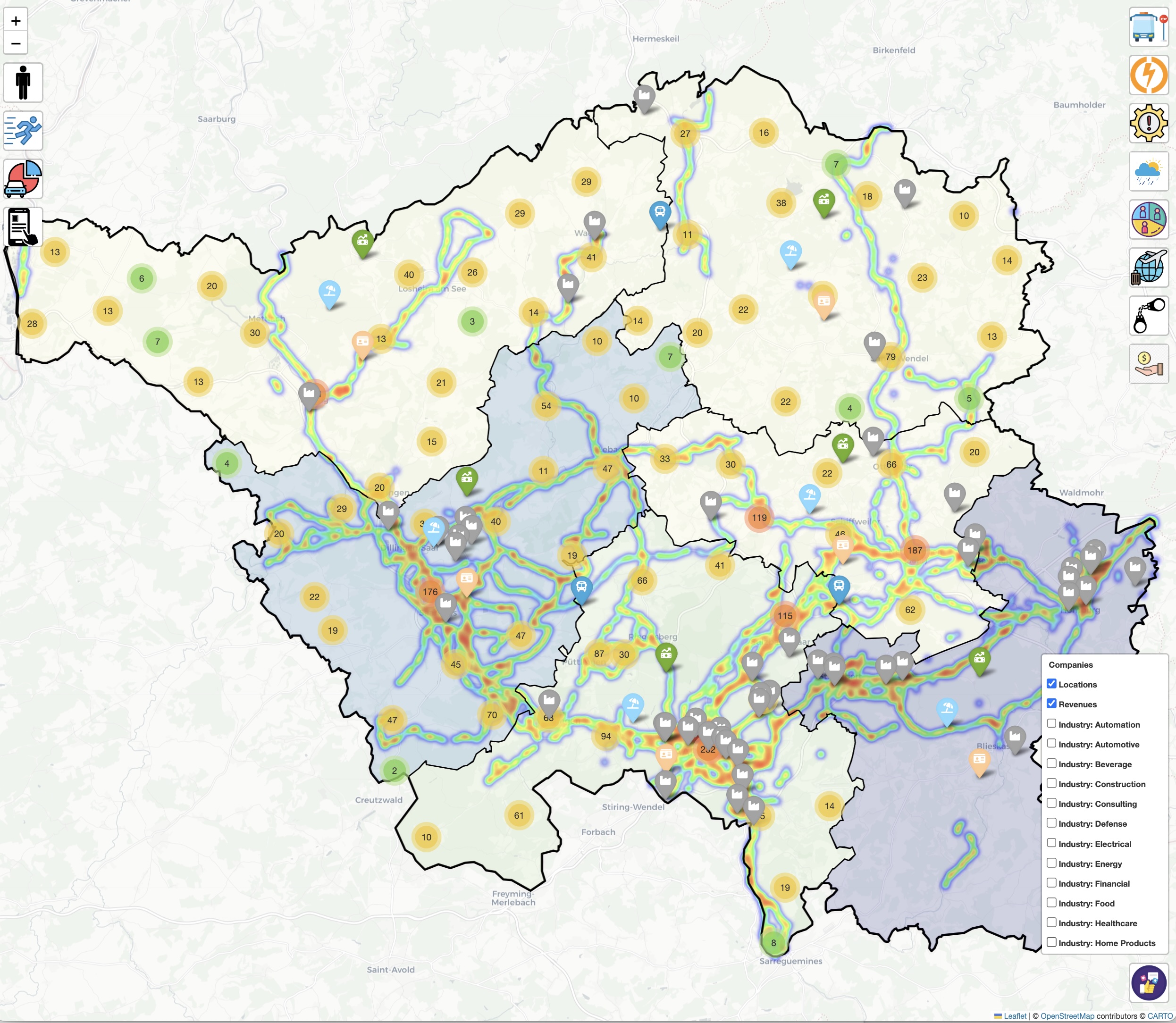
|
Mobility in rural areas often revolves around individualized solutions, such as private cars, creating challenges such as traffic congestion, environmental strain, and restricted access for socially disadvantaged and physically impaired individuals. To address these issues, the INTE:GRATE project is setting out to transform mobility in Saarland by offering groundbreaking transparency and data-driven decision support for policymakers, businesses, and public transportation providers. The project aims to analyze and understand the current state of system transport in Saarland, offering insights into the factors driving strong individualization in rural mobility. By leveraging innovative AI-based services, INTE:GRATE will provide actionable recommendations to shift from individual to system-oriented mobility, focusing on inclusivity and efficiency. Through aggregating diverse data streams—including movement data, demographic trends, mobility app usage, infrastructure data, and economic indicators—INTE:GRATE will distill this information into district-level insights. The project will identify mobility patterns and influencing factors, enabling smarter traffic bundling, enhanced mobility efficiency, and strengthened social and cultural participation, particularly for marginalized groups. Key objectives of the INTE:GRATE project include: - A detailed analysis of current transport systems in Saarland. - Development of AI-driven decision support tools to guide stakeholders. - Tailored recommendations to improve system mobility and ensure equal access for all citizens, regardless of their physical or social status. Presentation of Results at the Saarland State Parliament The project reached an important milestone today as its preliminary results were presented to the Transport Committee of the Saarland State Parliament by Prof. Wolfgang Maaß. This presentation marked a significant step in fostering dialogue with policymakers and stakeholders, providing them with actionable insights and recommendations to drive meaningful change in regional mobility. The outcomes of this initiative promise a mobility revolution in Saarland, paving the way for a sustainable, inclusive, and efficient transportation future. Collaboration and Funding The INTE:GRATE project is a collaborative effort with the HTW University of Applied Sciences and is funded by the European Regional Development Fund (EFRE) of the European Union.
Published on: 2025-02-14
🔗
|
| Keynote: The Future of AI in Europe: How AI Changes the Economic Landscape | |

|
Berchtesgaden, January 2025 – At the prestigious valantic Digital Excellence Forum 2025, Professor Wolfgang Maaß delivered an insightful keynote on the future of artificial intelligence in Europe and its profound impact on the economic landscape. The event brought together industry leaders, AI researchers, and digital transformation experts to discuss cutting-edge developments in AI and their implications for businesses and society. Professor Maaß began his talk with an overview of the industrial and scientific state of the art in AI, highlighting key advancements in deep learning, reinforcement learning, and explainable AI. He emphasized how AI is no longer an emerging technology but a critical driver of industrial innovation and economic transformation. A major highlight of his presentation was the discussion on Deepsearch R1, an AI breakthrough that had been released just days prior. Professor Maaß provided an analysis of its capabilities and potential applications, demonstrating how such advancements are accelerating the integration of AI into business intelligence, automation, and research processes. Following this, he turned to AI agents and their increasing importance across industries. He explained how AI-driven autonomous systems are reshaping supply chains, financial markets, healthcare, and manufacturing, driving efficiency and innovation. He emphasized that companies need to adapt quickly to leverage AI’s potential, or risk falling behind in a rapidly evolving digital economy. The final section of his talk focused on the future of AI and Quantum Machine Learning (QML). Professor Maaß outlined how QML could revolutionize optimization problems, material discovery, and financial modeling, paving the way for unprecedented computational capabilities. While quantum computing is still in its early stages, he stressed that companies and researchers should already be preparing for its transformative effects. Concluding his presentation, Professor Maaß offered an optimistic outlook on Germany’s position in AI research and startups. He highlighted the strong academic foundations, vibrant AI ecosystem, and increasing investments in AI-driven ventures, positioning Germany as a key player in global AI innovation. The valantic Digital Excellence Forum 2025 proved to be a crucial platform for discussing the future of AI in Europe. Professor Maaß’s keynote left attendees with valuable insights into the rapid advancements in AI, the strategic importance of AI agents, and the transformative potential of quantum computing. His final remarks reinforced the positive trajectory of European AI development, urging businesses and policymakers to embrace AI-driven opportunities for sustainable economic growth.
Published on: 2025-02-06
🔗
|

